The next issue to fix was another instruction check, this one after a console input instruction finished where the number of input characters was less than or equal to the number of expected input characters.
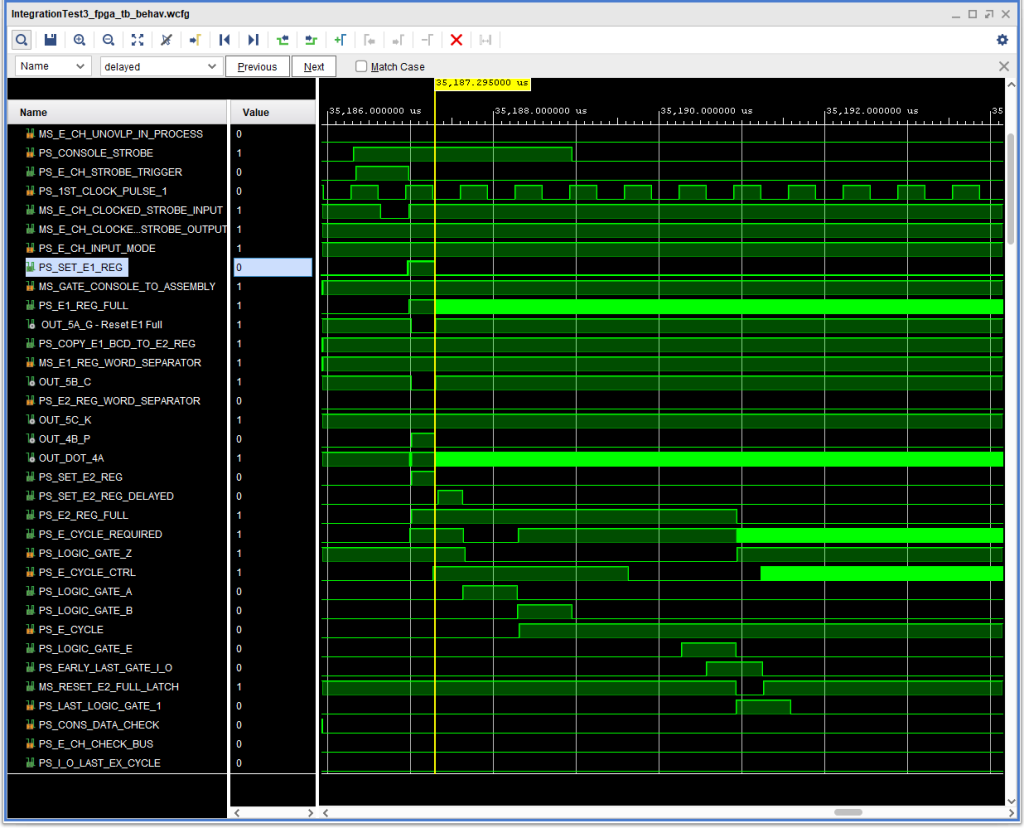
The basic problem was that as I/O was ending, the I CYCLE CTRL signal goes active while E CH UNOVERLAP IN PROCESS is also active.
The problem can be seen in this waveform capture:
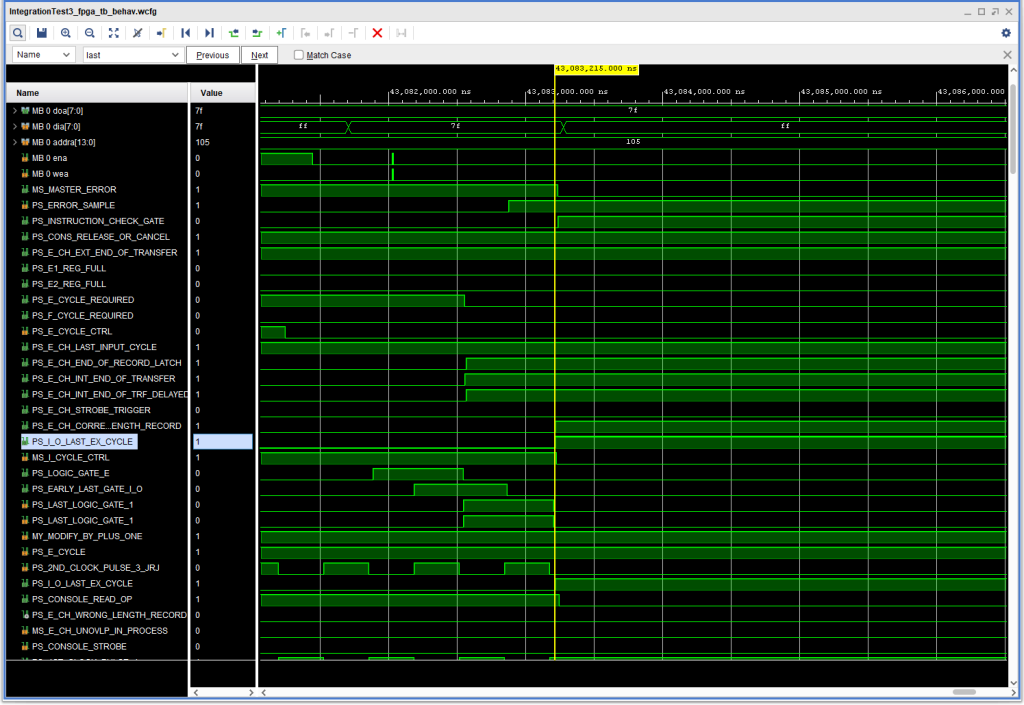
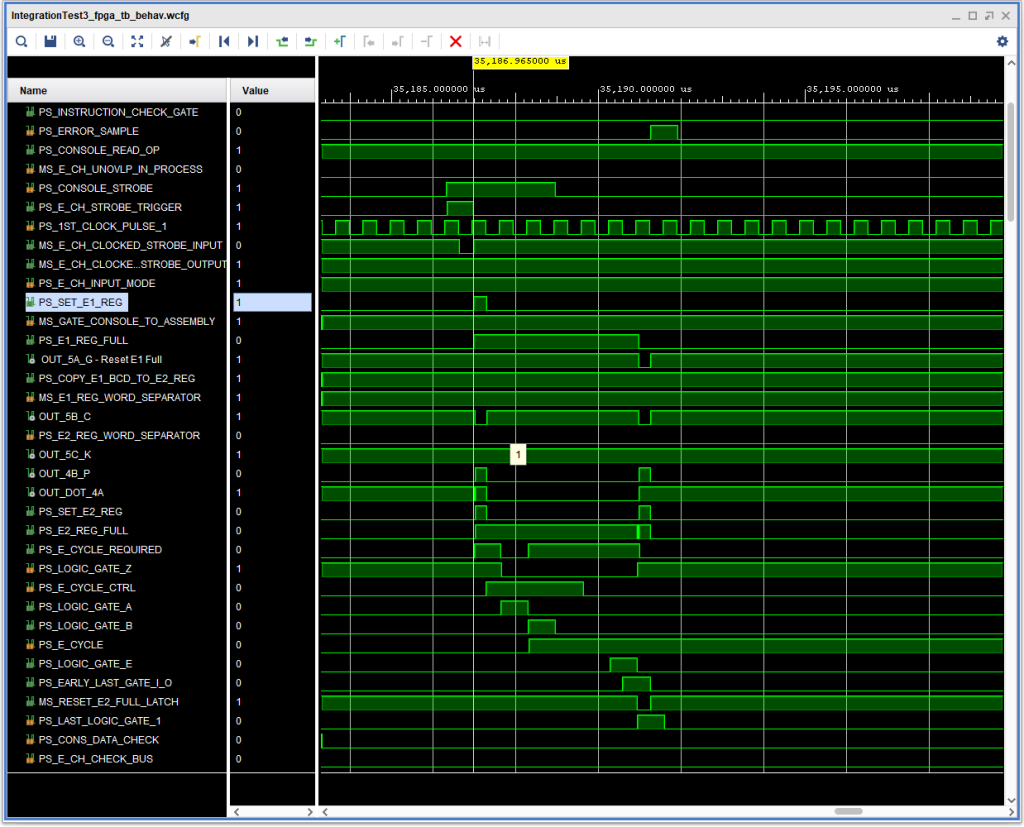
What made this problem a bit more interesting was that this error did not occur if the number of characters entered was more than the available buffer (i.e., from the address specified in the read instruction up to and not including the group mark with a word mark that marks the end of the input buffer:
I spent quite a few days looking at this and that and trying this and that, without making much headway. And in the process I discovered a couple of interesting errors in the IBM CE documentation for the 1410.
One thing I noticed was that the logic for an Instruction Check that is shown in the IBM 1410 System Fundamentals manual, S223-2589 and is quite simple would not have caused this Instruction Check, and that the logic in the Instruction Logic Diagrams, R23-2936 does have logic that would trigger an error under these circumstances and is more complex. The latter matches (more or less — more on that later) the ALD and triggers this error from either of the bottom two sets of (ILD) AND/OR gates in the lower left hand corner of Figure 58 of the ILD. (In reality, these are implemented using AND/NOR gates – aka And/Or/Invert gates).
The second thing I noticed was that in the I-O sequence diagram on page 43 of the 1411 I/O Operations Manual 223-2692 depicts +S I CYCLE CTRL indeed overlapping +S E CH UNOVERLAP IN PROCESS – in contradiction to what is on the ILDs.
Finally, in comparing the ILD to the ALD I did spot one error in the ILD. In the bottom most And/Or gate on the ILD, there is an OR gate for signals E CH OVERLAP IN PROCESS and I CYC CTRL. In fact, that one is F CH on the ALD (which make more sense).
So, what to do. I had some concern that the change I made earlier to ALD page 12.12.62.1 to inhibit E Cycle Required during Logic Gate A might be a problem, but thought experiments didn’t bear that out. Also, the condition seemed to be benign, in that once the I/O completed, E CH UNOVERLAP IN PROCESS would be de-asserted. Finally, I wondered it this might be another case where the speed of the FPGA logic for multiple layers via LUTs – look up tables – might be causing a race condition.
In the end, I decided on a simple approach. I created a variant of card type DHL, called DHLJ, with an extra direct input to the NOR gate, using otherwise unused pin K. I then fed in the I-O LAST EXEC CYC signal into ALD logic blocks 4E and 4H, which resolved the Instruction Check.
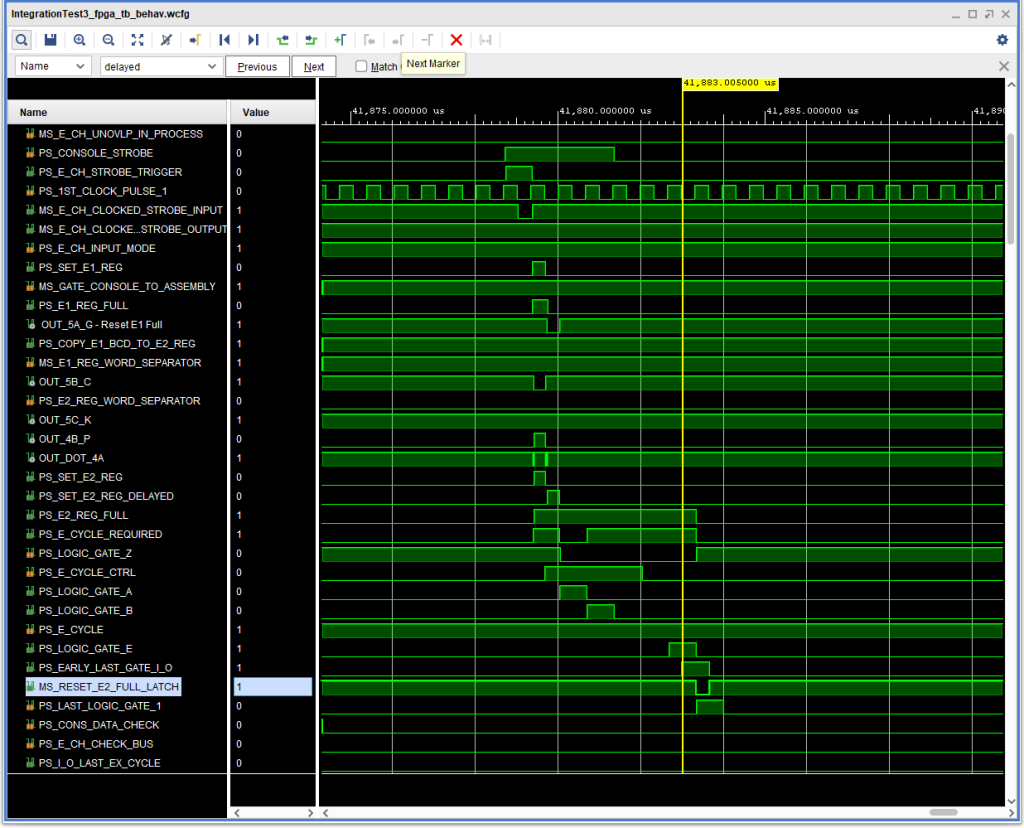
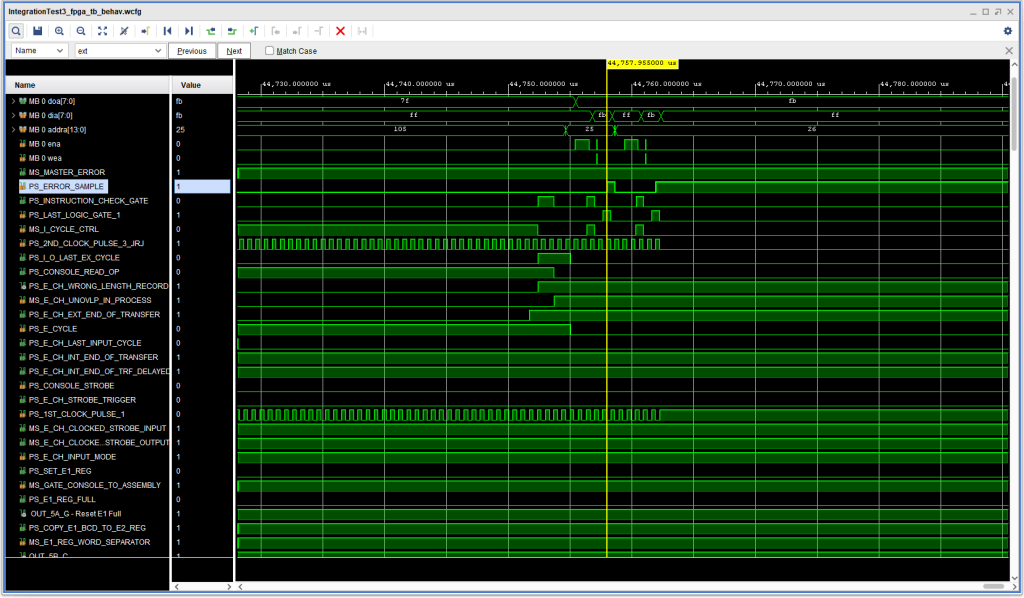
This is shown in the following timing diagram:
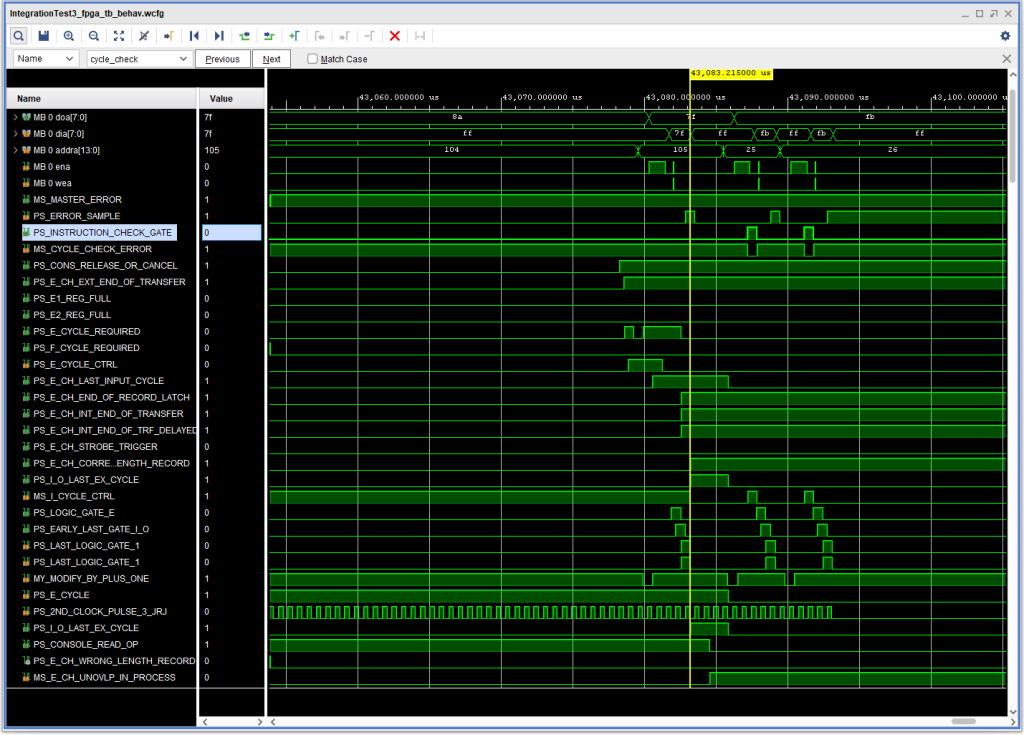
This isn’t the most satisfactory thing in the world, but given the contradictory nature of the IBM materials, I didn’t feel like I’d be able to sort it out properly – at least for now. (Also note in the above timing diagram the “notch” in +S E CYCLE REQUIRED during Logic Gate A, caused by the earlier fix.)
With this fix, there are no more problems running the 1410 diagnostic CU01C, nor the 1401 Mode diagnostic M011, including console input.
There is still much to do, including replicating the E Channel fix to ALD 15.41.10.1 into the F channel. After that, I think I will spend some time cleaning up console operations, where there are lots of things to change on the PC Support program software side, as well as some hardware issues, like the improper prompt character during the start of a console Display operation (and other operations as well), and some possible issues during address set and storage load and regen operations.